Proctology in Berlin - hemorrhoid, anal fissure and fistula surgery
Your competent partner for anal fissures, anal fistulas, anal skin tags and hemorrhoids in Berlin
Our practice for proctology (rectal diseases) with its sympathetic team of specialized doctors offers you an individual and highly qualified diagnosis and treatment of diseases in the rectal area and anus.
As experts in this field, we know how to deal empathetically with your natural fear and shame so that you can be relieved of your problems.
Our goal as a trained proctologist is to avoid surgery and to be your adequate contact during therapy.
Therefore, we specialize in low-pain, minimally invasive forms of therapy to get you back to work quickly. The treatment of hemorrhoids, anal fissures and anal fistulas is a main focus of our practice. With our location in Steglitz (Lankwitz), we are your competent contact for Berlin, Potsdam and Brandenburg. We look forward to seeing you.
proctology.berlin
Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are a part of our body and belong in the rectum like the fingers on the hand. It is not a disease. The word hemorrhoid is composed of the Greek words "haima" (blood) and "rhoos" (flow). Anatomically, hemorrhoids are blood-filled erectile tissue under the mucosa of the lower rectum. The main function of these erectile tissues is to seal the mucus-forming rectum (or rectum), from the dry anal canal. This fine closure function of the hemorrhoids accounts for about 15% of our continence organ and is therefore very useful.
The hemorrhoidal disease
Only when the hemorrhoids enlarge or when symptoms begin do we speak of hemorrhoidal disease as a clinical picture. Hemorrhoidal disease is one of the most common diseases in industrialized nations, and in Germany approximately 3.3 million patients are treated by physicians each year.
The peak incidence of hemorrhoidal complaints is between the ages of 45 and 65. Hemorrhoidal disease affects women and men about the same. The positions of hemorrhoids are described from the point of view of the doctor in front of the patient and are found at 3, 7 and 11 o'clock. Therefore, it is always 3 nodes.
Unlike other diseases of the anus and rectum, hemorrhoidal disease usually does not cause pain. The enlargements are often noticeable by bright red blood deposits on the toilet paper or painless bright red bleeding from the anus.
Other symptoms may include mucus flow from the anus, itching, burning, oozing and a foreign body sensation. In advanced stages, fecal smearing may also occur due to inadequate closure.
Therapy for hemorrhoids

Grade 1

Grade 2

Grade 3

Grade 4
If the change of behavior of patients is not enough, the help of the doctor or better proctologist is needed. These are specially trained doctors (surgeons, dermatologists, gastroenterologists) for all diseases and conditions in the rectal area.
Grade 1 and 2 hemorrhoids can be treated without surgery using minimally invasive therapy with rubber band ligation or sclerotherapy. However, it is important here to continue a high-fiber diet and greater fluid intake to prevent recurrence (recurrence) of the symptoms.
Grade 3 and 4 hemorrhoids (about 10% of patients with hemorrhoidal disease) require surgery. A basic distinction is made between hemorrhoid removal such as the Milligan-Morgan operation, lifting and shirring of the hemorrhoids (hemorrhoidopexy) such as the stapling procedure according to Longo, and hemorrhoid closure with suturing and shirring (HAL-RAR).
We also offer the particularly gentle minimally invasive procedures of radiofrequency ablation (Rafaelo) and laser therapy (LHP), which can be used for grade 2 and 3.
Anal fistula
Anal fistulas usually develop as a result of inflammation in the area of the so-called proctodeal glands in the rectal region. These glands are located at the transition of the colon mucosa to the anal canal. While they play an important role as scent glands in mammals, they have lost their function in humans.
Since the glands open into the interior of the intestine, bacteria from the intestine can invade the glands and cause an infection. As a result of this infection, purulent secretion is formed, which can become encapsulated and thus lead to a perianal abscess.
If this small abscess, which often does not cause any symptoms, persists for a longer period of time, ducts (fistulas) can form up to the skin surface due to the chronic inflammation. Less commonly, they may also extend into the urinary bladder or vagina. In some cases, a fistula also ends blindly in the tissue as a "blind alley." A Pilonidal sinus, on the other hand, is a separate clinical picture and has no connection to the anal canal.
Anal fistulas can also occur as a consequence of a chronic inflammatory bowel disease such as Crohn's disease or diverticulitis. Fistulas occur more frequently between the ages of 30 and 50, with more men being affected because they have more glands.
An anal fistula often makes itself felt for the first time as an abscess in the anus area (so-called perianal abscess), which must be cleared out under general anesthesia as an emergency. Only rarely can a fistula be visualized at this acute stage, as the tissue is severely swollen and friable.
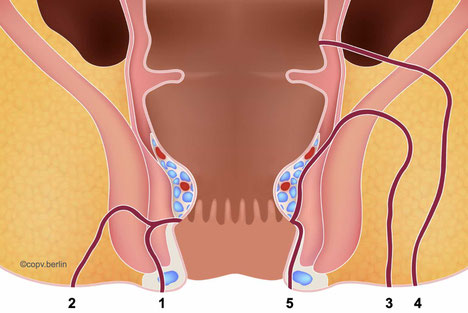
Anal fistulas are classified in relation to the sphincter muscle.
Important anatomical structures are the internal and external sphincter muscle and a serrated line (linda dentata), which lies approx. 2 cm inside the anal canal.
However, it is not always possible to clearly classify them into the appropriate type.
Does an anal fistula always require surgery?
An anal fistula always requires surgery and never heals spontaneously.
However, a fistula can cause no symptoms or only minor symptoms for a long period of time, i.e. be silent. Symptoms are usually oozing around the anus, which leads to soiling of the underwear and can also smell strongly. Often, a small gross swelling around the anus can also be felt.
An untreated fistula can lead to damage to the sphincter muscle due to recurrent inflammation with abscess formation and, in rare cases, to malignant degeneration. The type of operation depends on the course of the fistula. The relation to the sphincter muscle is of decisive importance for the choice of therapy.
What are the surgical procedures?
Due to the different location of anal fistulas to the sphincter muscle, there is a wide variation of surgical procedures. These are sometimes very painful and associated with a long wound healing, after which, however, the disease recurs less frequently. In contrast, there are less painful, minimally invasive procedures, which are quite unproblematic during surgery, but more often lead to recurrences.
Therefore, it is very difficult to predict the perfect procedure before a planned surgery. This is the reason why patients are usually fully informed about several surgical options, such as fistula splitting, flapplasty (flap) or thread drainage. Only under anesthesia can the fistula tract be diagnosed with its length and course by means of probes, and only then is the appropriate therapy decided. Since the patient is anesthetized, he cannot be asked about this, which is why this freedom of choice of the surgical method is assured by the patient to the surgeon in the explanatory talk before the operation.
It should be noted that all operations should be performed under general anesthesia in order to provide optimal therapy. An examination of the duct is very painful and usually has to be stopped after 1cm.
Anal fissure
Anal fissures are small tears in the very painful anal skin (anoderm), often caused by hard stool or strong pressing.

The leading symptom here is the burning pain during defecation and 1-2 hours afterwards. Since anal fissure is a laceration, larger amounts of blood may also be discharged. Patients often report a painful tearing of the anal skin.
The pain can become so severe that patients avoid defecation and become constipated, which worsens the situation. A cycle begins that must be stopped.
We have a great experience in the treatment of anal fissure especially in young people and we always try to avoid surgery. However, if surgery is necessary, we perform it safely, with little pain and without complications. Do not be afraid and trust us.
When should surgery be done?
If conservative therapy with ointment does not lead to healing and the complaints limit the quality of life, surgical therapy should be considered. In Germany, fissurectomy under anesthesia is the preferred procedure. During the operation, which can usually be performed on an outpatient basis, the anal fissure with its secondary formations (outpost fold and hypertrophic anal papilla) is completely excised. An open wound remains, which also releases wound secretions in the following 4-6 weeks. There is no risk to the sphincter muscle with this procedure, as only a very small scarred upper layer of the sphincter muscle has to be removed as well, which does not affect its function.
The aim of this operation is to obtain a fresh wound tissue, which can also grow together well. Pain is always present and can last in varying intensity for up to 3 weeks. Taking painkillers during the first 3 days is therefore particularly important. It is also essential to prevent constipation. To achieve a better effect, the operation can be combined with BOTOX therapy. This operation should only be performed by proctological experts to avoid injury to the sphincter muscle.
Laser Therapy (LFC) for Anal Fissures
Laser Fissure Cleaning (LFC) - a new treatment for anal fissures
In gentle laser therapy, the fissure is obliterated with particular precision using targeted heat.
The penetration depth and damage to the internal sphincter muscle is very low, which leads to significantly less pain in the healing phase.
The advantages
- The risk of incontinence is greatly minimized.
- The treatment is generally perceived as very painless.
- Severe scarring is avoided to a large extent.
- The risk of infection is significantly reduced due to the reduced trauma.
Anal vein thrombosis
Anal vein thrombosis is a sudden event and can be very painful. It is a small blood clot in veins that run under the skin in the anal area. Synonyms include "anal thrombosis, perianal thrombosis, or perianal venous thrombosis." Mistakenly, the term "external hemorrhoid" is often used, but this is anatomically incorrect, as hemorrhoids are located in the anal canal, not on the outside.

Anal vein thrombosis is an acute vascular occlusion in the anus that occurs suddenly.
The clotted blood causes a typical bluish-purple swelling, which can cause pain due to the taut skin.
Due to its external location at the edge of the anus, the thrombosis can be easily felt, in contrast to internal hemorrhoids.
What does the therapy look like?
Anal venous thrombosis does not require surgery because the blood clot dissolves completely. Therefore, only analgesic measures are required, such as ointments and gels with lidocaine and anti-inflammatory painkillers such as ibuprofen or diclofenac. Thrombolytic ointments have no effect on the course.
After 2-5 days, the pain usually subsides significantly. Tension decreases as the skin softens again (regression of edema). The breakdown of the blood clot can take up to 6 weeks, depending on its size, but by then there is no longer any pain.
In the case of very large thromboses, the skin may burst open due to the strong pressure and bleeding with black crumbs may occur, which corresponds to clotted blood. This causes an abrupt relief. The wound then only needs to be blotted out with water 2x a day and 'heals without any problems.
It is important to note that anal thrombosis is a small occlusion of a blood vessel and this blood clot (thrombus) cannot travel further, i.e. it cannot become an embolism! Most people have had anal venous thrombosis in your life, so it is a very common phenomenon.
more information about anal vein thrombosis...
Anal skin tag

Anal skin tags are small skin folds that are skin colored and can form around the anal margin. Their consistency is usually soft, but can also take on quite coarse forms. Marisques can vary greatly in size, from the size of a pinhead to an olive. Anal skin tags can occur singly or as a ring that encircles the entire anus.
However, the formerly used name external hemorrhoids is incorrect and should no longer be applied, since hemorrhoids are vascular cushions and not skin folds. They are usually always harmless and do not cause any discomfort.
The diagnosis is made by sight, no further examinations are necessary.
What is the therapy of Anal skin tags?
Anal Tags that are asymptomatic, i.e. do not cause any symptoms, do not require therapy. However, if recurrent inflammation and problems with anal hygiene occur, mariscs can be removed. This can usually always be done on an outpatient basis. Individual marisci should be removed under local anesthesia by proctologists or proctological surgeons. The resulting wounds always remain open and heal after 2-4 weeks. If the wound is blotted out with water twice a day, there is no risk of infection.
If there are several mariscs or the mariscs extend deeper into the anal canal, it is better to perform the removal under short anesthesia due to the extensive local anesthesia.
In the case of a ring of mariscs, caution should always be exercised due to possible constriction caused by scarring, and adequate skin bridging must be maintained.
Before surgery, a complete proctological examination such as a proctoscopy and, if necessary, rectoscopy should always be performed to rule out other diseases in the anal region.
more information about anal skin tags...


